We all have Wi-Fi and network connection problems today. When it comes to using public networks where there is a huge traffic, using Wi-Fi almost seems impossible.
We find it difficult to connect our devices to the public networks or experience very slow speeds.
Initially, when you would look for Wi-Fi signals where a large public resides, it is hard to connect with the network as there were so many users fighting for the same network that had a limited spectrum.
No bandwidth could manage the traffic of users trying to use the internet at the same frequency of connection levels, which ultimately led to the frustration of users.
However, a solution to this problem has been developed by the team of researchers at MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL). The solution brought to this issue was ‘Real Time Distribute MIMO system’ which was described by the team as management of networks that enable the Wi-Fi router to collaborate in a better way.
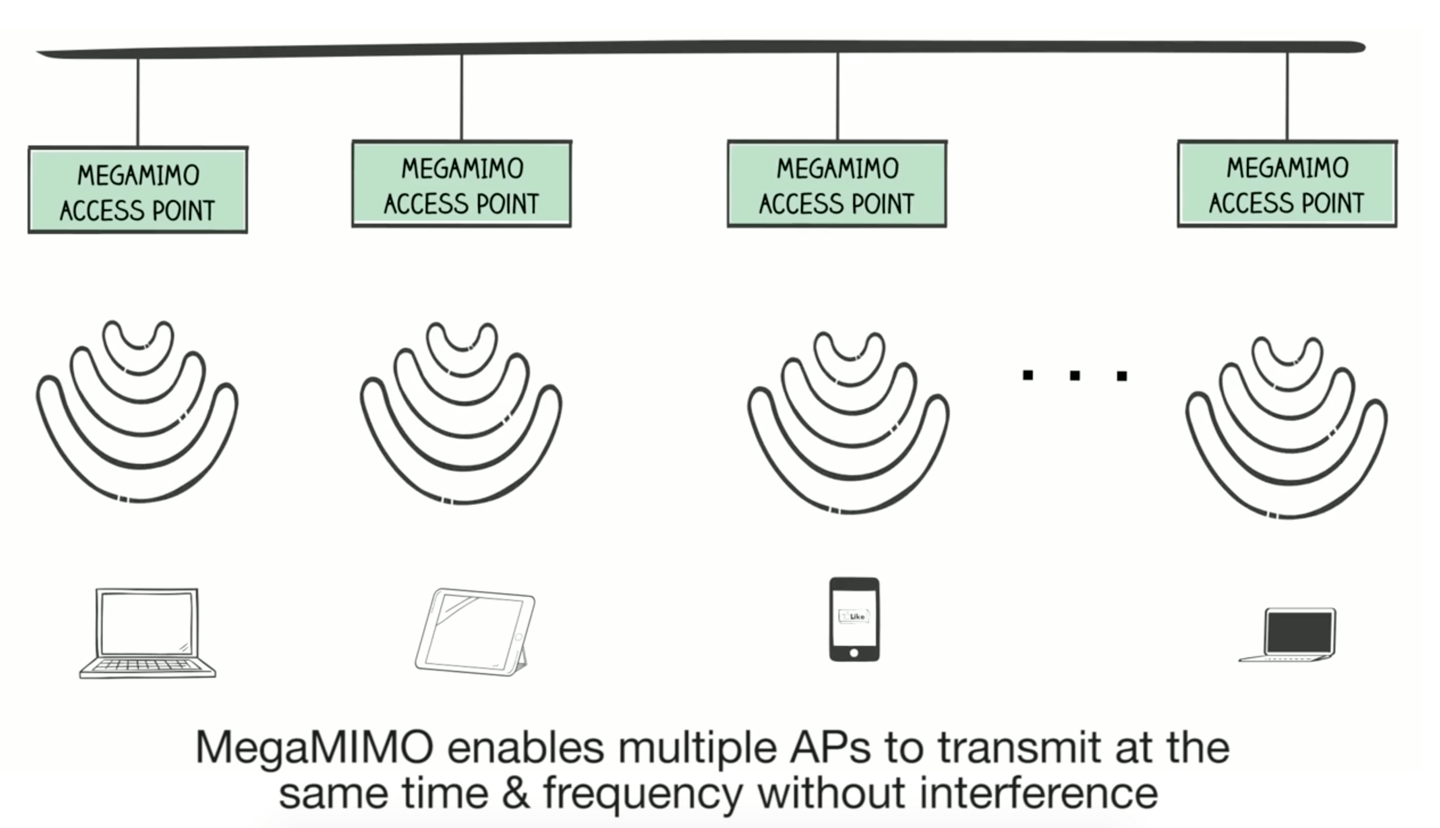
This new wireless system “MegaMIMO” has brought a great change that has solved Connectivity problems at public WiFi hot-spots to a very great extent.
The Multiple Input Multiple Output technology (MIMO) can provide three times faster internet access to the networked devices by offering a combination of multiple transmitters which enables to users experience more than one available network at a time. In the MIMO system, many routers work together by offering data over the same piece of spectrum.
Thus, MIMO 2.0 has emerged as a system that has managed to coordinate multiple routers at one time which syncs their phases to enable transmission of the same spectrum by multiple transmitters without causing any interference.
This project was successfully funded by the National Science Foundation and had strong support from the members of MIT center for Wireless Networking and Mobile Computing.
This is How it works..
One might wonder how smartphones have experienced better speeds because of MIMO. This is because the MIMO uses a number of routers to spread the spectrum to many users at the same time.
Here the radio waves bounce off the surfaces and reach the users at little differentiated times with multiple users helping them to use data better and faster.
CSAIL found a technique to connect multiple transmitters by harmonizing their phases. They established special signal processing conclusions to enable multiple transmitters to send data on the same piece of spectrum to a large traffic without inventing any conflicts.

It is also believed that this technology can help the cellular networks where similar congestion problems can be solved by the people who use their phones for calling purposes.
The team looks forward to expanding this technology where they can develop a connection of multiple routers at once. This is helping them transmit faster data speeds in an area with heavy traffics.
This solution will be very useful in campuses and enterprises where the current solutions have been so slow and a spotty performance.
The technology defiantly has the potential to perform better and serve better to the people. It has the potential to provide higher speeds of the network to each and every user.
The researchers of MIT team announced that in a big crowd, MegaMIMO 2.0 manages to transfer wireless data 3.6 times better and faster than the usual systems.
They also mentioned that when additional tests were created with number or routers, the speed raised to 10 times better. They believe to have a successful MegaMIMO startup, which has been working and exploring more on commercializing the technology and help the traffic get benefit from this technology.
Source: news.mit.edu